Grade 8 Math Standards

Rotate, Reflect And Translate Angles
Angles are taken to angles of the same measure.

Understand Systems Of Equations
Understand that solutions to a system of two linear equations in two variables correspond to points of intersection of their graphs, because points of intersection satisfy both equations simultaneously.

Unit Rate As Slope Of A Graph
Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare a distance-time graph to a distance-time equation to determine which of two moving objects has greater speed.

Algebraic Expressions using Distributive Property
Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms.

Rotate, Reflect And Translate Parallel Lines
Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines.
Puppet Kid & The Book of Motions

Create Tables to Compare Data
Understand that patterns of association can also be seen in bivariate categorical data by displaying frequencies and relative frequencies in a two-way table. Construct and interpret a two-way table summarizing data on two categorical variables collected from the same subjects. Use relative frequencies calculated for rows or columns to describe possible association between the two variables. For example, collect data from students in your class on whether or not they have a curfew on school nights and whether or not they have assigned chores at home. Is there evidence that those who have a curfew also tend to have chores?

Understand Irrational Numbers
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number.
Irrational Space Problem
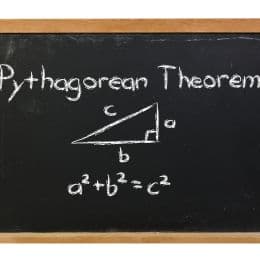
Apply Pythagorean Theorem To Find Missing Side
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions.
Pythagoras to the Rescue
Describing Functions
Describe qualitatively the functional relationship between two quantities by analyzing a graph (e.g., where the function is increasing or decreasing, linear or nonlinear). Sketch a graph that exhibits the qualitative features of a function that has been described verbally.

Properties of Rigid Transformations
Lines are taken to lines, and line segments to line segments of the same length.

Volume of 3D Figures
Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems.

Compare Irrational Numbers Using Approximations
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π^2). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.

Solve Problems with Slope-Intercept Equations
Use the equation of a linear model to solve problems in the context of bivariate measurement data, interpreting the slope and intercept. For example, in a linear model for a biology experiment, interpret a slope of 1.5 cm/hr as meaning that an additional hour of sunlight each day is associated with an additional 1.5 cm in mature plant height.

Integer Exponents
Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, (3^2) × (3^-5) = (3^-3) = (1/3)^3 = 1/27.
Domino2

Understand Algebraic Results
Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers).
Algebraic Monkey

Solve Real World Problems With System Of Equations
Solve real-world and mathematical problems leading to two linear equations in two variables. For example, given coordinates for two pairs of points, determine whether the line through the first pair of points intersects the line through the second pair.

Similarity Through Transformations
Understand that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations; given two similar two-dimensional figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the similarity between them.
Solve Systems Of Equations
Solve systems of two linear equations in two variables algebraically, and estimate solutions by graphing the equations. Solve simple cases by inspection. For example, 3x + 2y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 6 have no solution because 3x + 2y cannot simultaneously be 5 and 6.

Congruence with Transformations
Understand that a two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given two congruent figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the congruence between them.
The Tangram Variety

Describe Transformation Using Coordinates
Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates.

Proof Of Pythagorean Theorem
Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.

Construct And Interpret Scatter Plots
Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and nonlinear association.

Linear Relationships
Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models, and in terms of its graph or a table of values.
Who Wants to be Functional?

Line Of Best Fit
Know that straight lines are widely used to model relationships between two quantitative variables. For scatter plots that suggest a linear association, informally fit a straight line, and informally assess the model fit by judging the closeness of the data points to the line.
Find the Spy
Understanding Functions
Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output.

Operations With Scientific Notation
Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology.
Slope-Intercept Form As A Function
Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. For example, the function A = s^2 giving the area of a square as a function of its side length is not linear because its graph contains the points (1,1), (2,4) and (3,9), which are not on a straight line.
Function Coaster

Find Square And Cube Roots
Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x^2 = p and x^3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational.

Pythagorean Theorem on a Coordinate Graph
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system.

Use Powers Of Ten To Estimate
Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3 times 10^8 and the population of the world as 7 times 10^9, and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger.

Compare Functions
Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). For example, given a linear function represented by a table of values and a linear function represented by an algebraic expression, determine which function has the greater rate of change.

Prove Consistency Of Slope Using Similar Triangles
Use similar triangles to explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane; derive the equation y = mx for a line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intercepting the vertical axis at b.

Analyzing Angles Inside and Outside of Triangles
Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, about the angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal, and the angle-angle criterion for similarity of triangles. For example, arrange three copies of the same triangle so that the sum of the three angles appears to form a line, and give an argument in terms of transversals why this is so.